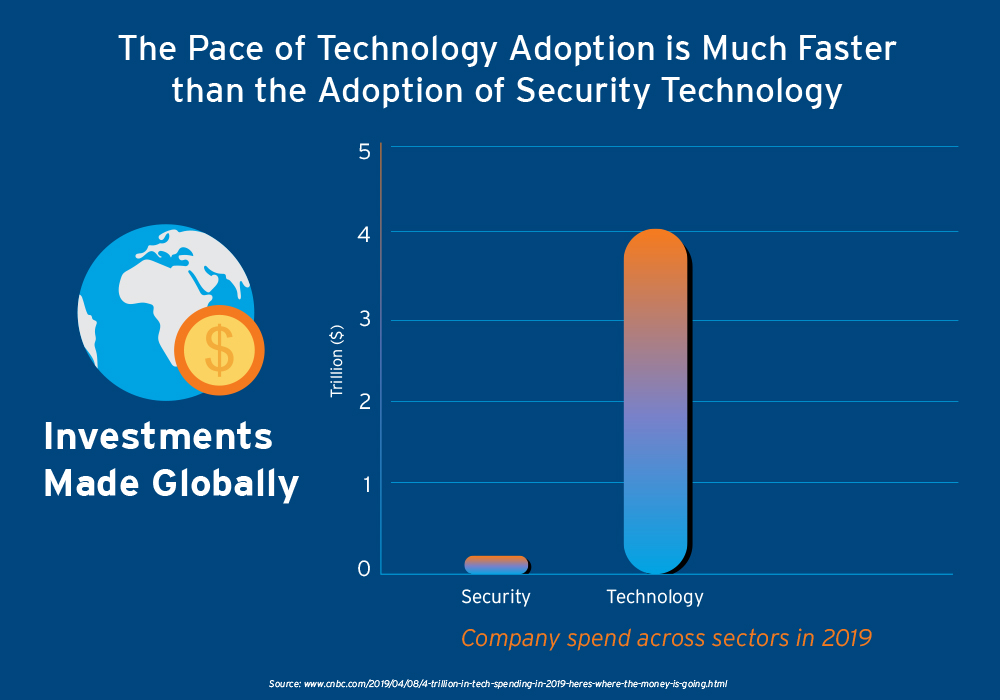
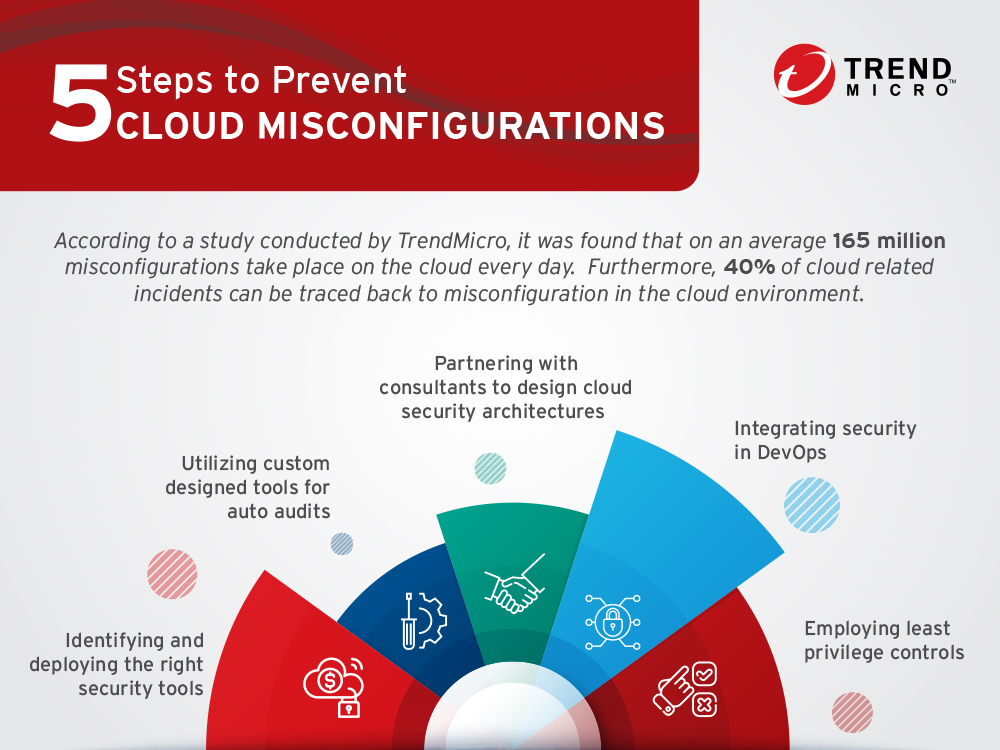
The entire world is navigating through the a crisis and the fallout of the global pandemic has upset political, financial, and economic structures worldwide.

Climate change is a bigger challenge that has been there for a long time and has the potential to impact every human, industry, and living organism on the planet.
Climate Change – Catastrophic impacts on our planet
Changing weather patterns, rising sea levels, and extreme weather events are some of the ways in which climate change is proliferating around the world. As per a developer survey conducted by IBM, 77 percent of the first responders and developers agreed that ‘climate change is indeed the most pressing issue faced by today’s generation’ [Source].
Another insightful study throws some light on preparedness for natural disasters. By 2050, the global population is expected to reach 9.5 billion people, which will put further pressure on the earth’s resources [Source]. Imagine a scenario where 100+ people are living in a small room, how cramped and suffocating it would be for those people?
The same thing will happen if the existing natural resources offered by the earth are not enough to serve living organisms on the earth. Apart from the impact caused on the natural resources on the earth, global warming has led to a rise in the overall temperature of the earth.
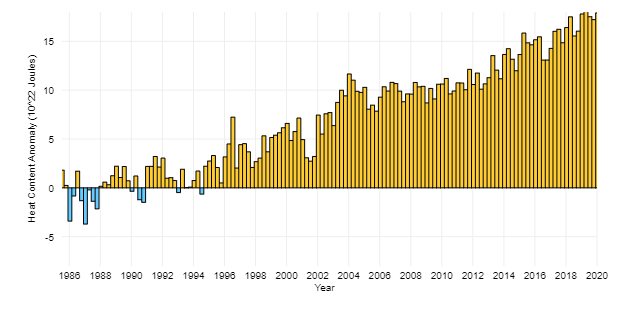
A growing amount of GHG [Green House Gases] are also preventing the heat radiated from Earth’s surface to escape into space. Due to this, the heat content in the upper ocean has increased a lot over the last two decades. By 2100, global temperatures could rise by 3-5 degrees Celsius [5.4~9.0 degrees Fahrenheit].
Technological solutions can be instrumental in combating climate change. In the past, IBM has taken significant strides by connecting humanitarian experts with talented developers across the world to keep a check on climate change. #CallForCode is one such initiative by IBM through which the company plans to identify and deploy technology solutions to create a better world for tomorrow.
#CallForCode 2020 – Focus on Prevention and Reversal of Climate Change
Call for Code is a global campaign that was started by David Clark Cause in 2018 and IBM has been the founding partner since the inception of #CallForCode. Call for Code is an initiative targeted towards developers, data scientists, and change-makers who intend to make this world a better place to live! They can catalyze their skills to create solutions using IBM tools.

Call for Code 2019 received a phenomenal response as over 180,000 participants from 165 nations participated in the hackathon focused on relief and natural disaster preparedness. Whopping 5000 applications were created in that edition of Call for Code [Source].
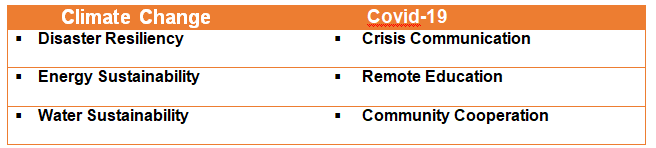
The tracks for #CallForCode 2020 are understandably #Covid-19 and #ClimateChange. Call for Code 2020 is an ideal platform for developers and change agents, as they get an opportunity to utilize their passion for creating technology solutions that can reverse the impact of climate change.
Development Tracks for #CallforCode 2020
The development tracks [or sub-categories] are more relevant than ever before:
IBM provides all necessary resources, tool kits, and products that can be used for creating meaningful solutions for combating climate change. Starter kits from IBM are ideal resources for understanding the scope of the problem and build applications in a short span of time. Climate Change enthusiasts can refer to starter kits, technical resources, and reference materials related to that topic here.
Steps to participate in #CallforCode 2020
For participating in #CallForCode 2020, perform the following steps:
- Accept the Challenge – Create your IBM Id & join the challenge by clicking on https://cloud.ibm.com/registration.
- Build with open-technology – Leverage available resources such as code patterns, expert videos, and tutorials for giving shape to your idea.
- Build a winning team – Leverage the community for getting support, in terms of finding teammates, meeting experts, asking questions, or simply sharing path-breaking ideas.
- Submit your idea – Submit details about the idea and the thought process that went into building the same. You also need to submit the participation agreement. The winner stands a chance to win a whopping $200,00.
Important Dates for #CallForCode 2020
- Final Submission Deadline – 31st July, 2020
- Announcement of Global Challenge Winners – October, 2020
- Prize – $200,000, Open source support from the Linux foundation, meetings with mentors and investors, and seeing their solution getting deployed through Code and Response to further exemplify using tech for good.